The global energy sector is in the midst of a transformative shift, fuelled by increasing demand for cleaner energy and the urgent need for more resilient and efficient power systems. At the heart of this evolution is the emergence of smart grids. These are advanced electricity networks that integrate digital technologies to optimise the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity.
As countries across the world advance their national energy strategies, smart grid implementation is fast becoming essential infrastructure. Yet, with technological innovation comes new challenges and opportunities, particularly when it comes to the workforce needed to manage and support this transition.
The adoption of smart grid technology is driving demand for a more tech-savvy workforce.
What Are Smart Grids?
Smart grids go beyond traditional energy systems by enabling two-way communication between utilities and consumers. These networks incorporate advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), automated control systems, distributed energy resources (DERs) like solar panels and wind turbines, and real-time data analytics to improve grid performance and customer engagement.
They rely on technologies such as:
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
- IoT (Internet of Things) sensors
- Artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analysis
- Cloud-based monitoring systems
This digital integration enables grids to respond dynamically to changes in electricity demand and supply, ensuring energy reliability, flexibility, and sustainability.
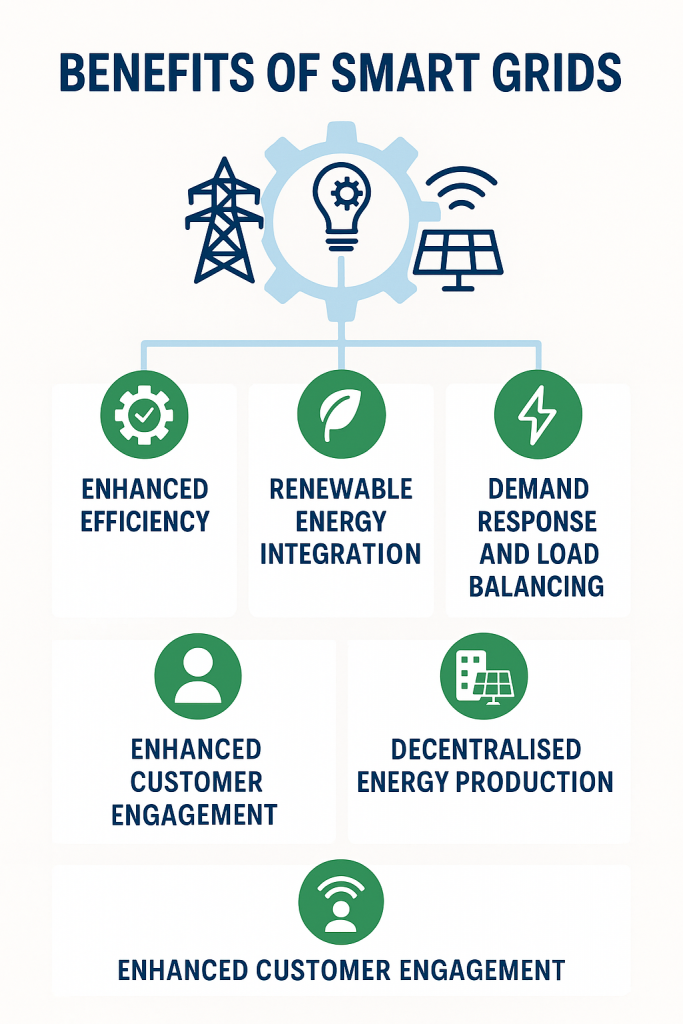
Benefits of Smart Grids
- Enhanced Efficiency and Reduced Losses
By minimising transmission and distribution losses, smart grids ensure more electricity reaches consumers with lower operational costs. Automated systems also identify and isolate faults more quickly, reducing downtime.
- Renewable Energy Integration
Smart grids facilitate a smooth incorporation of renewable energy sources by managing intermittent supply through real-time adjustments and battery storage solutions. This is essential for companies and governments aiming to reach net-zero emissions targets.
- Demand Response and Load Balancing
Consumers and utilities alike benefit from real-time pricing and energy usage data. This allows for smarter decision-making, incentivises off-peak usage, and balances grid demand.
- Decentralised Energy Production
Smart grids support microgrids and distributed generation, empowering communities and businesses to produce their own electricity and feed surplus back into the grid.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement
Smart meters offer users detailed insights into their consumption habits, enabling them to reduce usage, save on costs, and participate in energy-saving initiatives.
Challenges in Smart Grid Implementation
Despite their potential, rolling out smart grids presents several hurdles:
- High Upfront Costs
Developing smart infrastructure requires substantial investment in digital hardware, communication protocols, and grid automation. - Cybersecurity Threats
Digital systems increase exposure to cyberattacks. Grid operators must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, from endpoint protection to AI-driven threat detection. - Complex Regulation and Standardisation
The lack of unified global standards makes it difficult to create interoperable systems across regions, particularly for multinational energy operators. - Data Management and Privacy
Handling vast amounts of real-time data introduces concerns around data governance, privacy rights, and ethical usage. - Skill Shortages
Smart grid systems require a workforce equipped with digital, analytical, and engineering capabilities. Skills not always abundant in traditional energy roles.
The Evolving Energy Workforce
The adoption of smart grid technology is driving demand for a more tech-savvy workforce. The roles that will be most in demand include:
- Electrical and Software Engineers with experience in automation and power systems
- Cybersecurity Specialists focused on critical infrastructure protection
- Data Analysts to interpret grid behaviour and forecast trends
- Renewable Energy Technicians for system integration and maintenance
- Field Technicians trained in smart meter installation and grid diagnostics
Governments and training institutions are now being called upon to bridge the skills gap. Upskilling programmes, apprenticeships, and industry-academic partnerships are crucial in building a future-ready energy workforce.
Case Study: Ireland and Saudi Arabia
Ireland
Ireland is rapidly expanding its renewable energy capacity, aiming for 80% renewable electricity by 2030. Smart grids are a cornerstone of this strategy, enabling more effective management of wind and solar inputs. Initiatives such as ESB Networks’ National Smart Metering Programme show the country’s commitment to grid modernisation.
Saudi Arabia
As part of Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia is shifting from oil dependency towards a sustainable energy model. Projects like NEOM are powered by 100% renewable energy and feature intelligent grid systems from inception, offering a glimpse into the future of fully digital energy ecosystems.
PE Global Energy: Supporting the Transition
At PE Global, we are proud to be a recruitment partner to the leading players in the energy sector. With specialist teams focusing on energy recruitment across the globe, we help clients secure the talent they need for today’s challenges and tomorrow’s ambitions.
Whether it’s placing electrical engineers for offshore wind projects or sourcing cybersecurity professionals for grid operators, PE Global Energy ensures that the people behind the technology are as future-ready as the systems they manage.
Conclusion
Smart grids are revolutionising how we generate, distribute, and consume energy. While implementation is complex and resource-intensive, the long-term benefits for sustainability, efficiency, and consumer empowerment are undeniable.
As these technologies reshape the sector, so too must the workforce evolve. The energy sector’s future lies in digital expertise, adaptability, and forward-thinking recruitment, areas where PE Global Energy is already delivering value. By embracing innovation and building strong industry partnerships, we can power a smarter, greener tomorrow.
